W. Central Juvenile Center serves 19 students in grades 6-12.
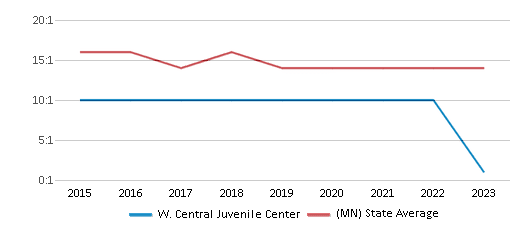
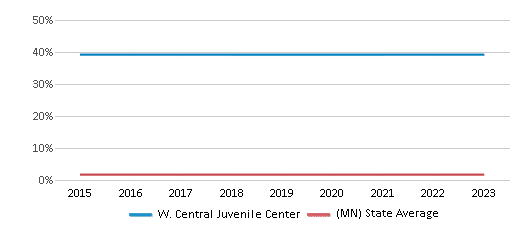
The student:teacher ratio of 10:1 was lower than the Minnesota state level of 13:1.
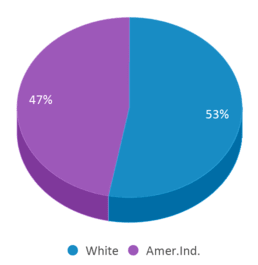
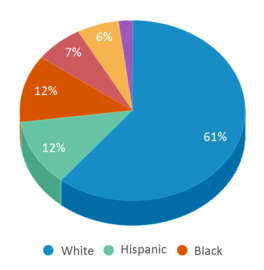
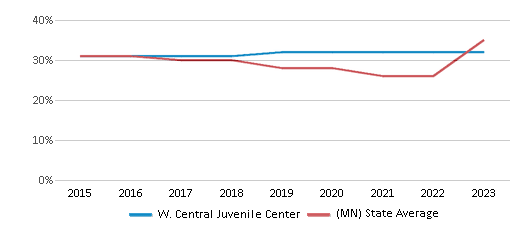
Minority enrollment was 47% of the student body (majority American Indian), which was higher than the Minnesota state average of 39% (majority Black).
School Overview
School Type
Grades Offered
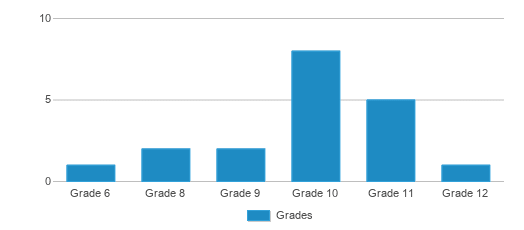
Grades 6-12
Total Students
19 students
Total Classroom Teachers
2 teachers
Students by Grade
School Rankings
Student : Teacher Ratio
10:1
13:1
American Indian
47%
2%
Asian
n/a
7%
Hispanic
n/a
12%
Black
n/a
12%
White
53%
61%
Hawaiian
n/a
n/a
Two or more races
n/a
6%
All Ethnic Groups
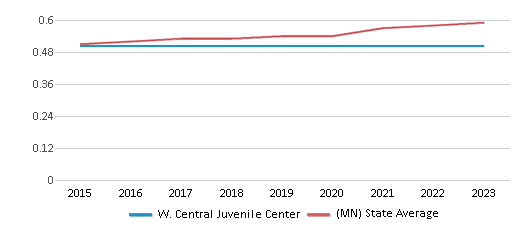
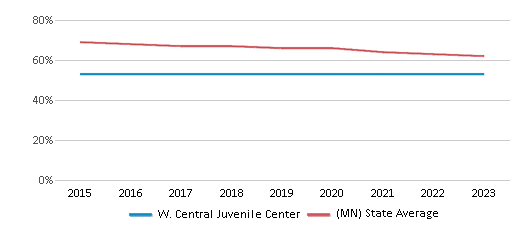
Eligible for Free Lunch
32%
36%
School Statewide Testing
School District Name
Source: National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), MN Dept. of Education
Frequently Asked Questions
How many students attend W. Central Juvenile Center?
19 students attend W. Central Juvenile Center.
What is the racial composition of the student body?
53% of W. Central Juvenile Center students are White, and 47% of students are American Indian.
What is the student:teacher ratio of W. Central Juvenile Center?
W. Central Juvenile Center has a student ration of 10:1, which is lower than the Minnesota state average of 13:1.
What grades does W. Central Juvenile Center offer ?
W. Central Juvenile Center offers enrollment in grades 6-12
What school district is W. Central Juvenile Center part of?
W. Central Juvenile Center is part of Moorhead Area Public Schools School District.
Recent Articles

What Is A Charter School?
Explore the world of charter schools in this comprehensive guide. Learn about their history, how they operate, and the pros and cons of this educational innovation. Discover key facts about charter schools, including admission policies, demographics, and funding, as well as what to look for when considering a charter school for your child.

10 Reasons Why High School Sports Benefit Students
Discover the 10 compelling reasons why high school sports are beneficial for students. This comprehensive article explores how athletics enhance academic performance, foster personal growth, and develop crucial life skills. From improved fitness and time management to leadership development and community representation, learn why participating in high school sports can be a game-changer for students' overall success and well-being.

February 05, 2025
Understanding the U.S. Department of Education: Structure, Impact, and EvolutionWe explore how the Department of Education shapes American education, from its cabinet-level leadership to its impact on millions of students, written for general audiences seeking clarity on this vital institution.





